Table of Contents
Role of Financial Intermediaries
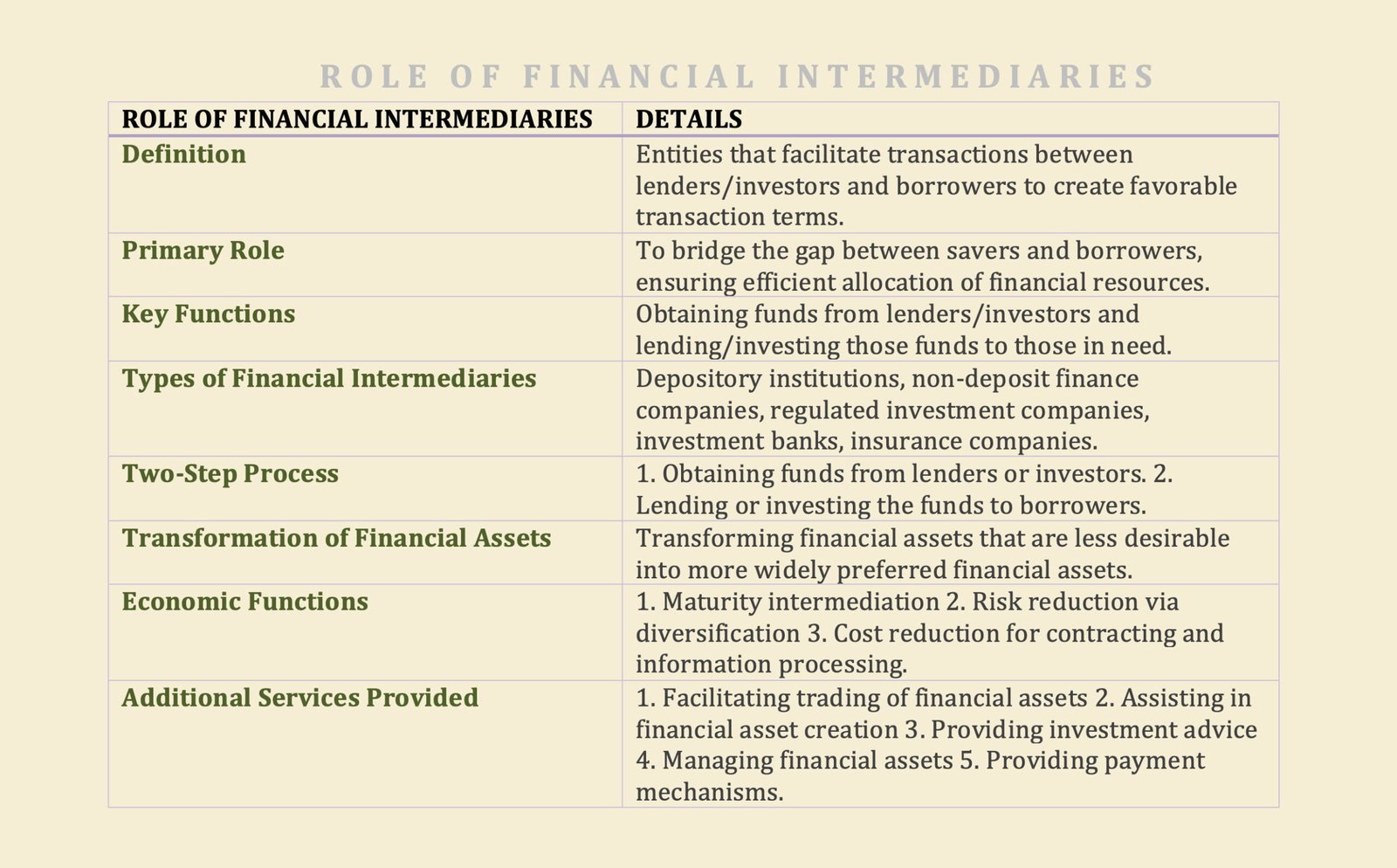
The role of financial intermediaries is to create more favorable transaction terms than could be realised by lenders/investors and borrowers dealing directly with each other in the financial market.
Financial intermediaries play a role in the efficient functioning of financial markets by bridging the gap between savers and borrowers.
Despite the important role of financial markets, their role in allowing the efficient allocation for those who have funds to invest and those who need funds may not always work as described earlier.
As a result, financial systems have found the need for a special type of financial entity, a financial intermediary, when there are conditions that make it difficult for lenders or investors of funds to deal directly with borrowers of funds in financial markets.
Financial intermediaries include depository institutions, non-deposit finance companies, regulated investment companies, investment banks, and insurance companies.
The role of financial intermediaries is to create more favorable transaction terms than could be realised by lenders/investors and borrowers dealing directly with each other in the financial market. Financial intermediaries accomplish this in a two-step process:
- Obtaining funds from lenders or investors.
- Lending or investing the funds that they borrow to those who need funds.
The funds that a financial intermediary acquires become, depending on the financial claim, either the debt of the financial intermediary or equity participants of the financial intermediary. The funds that a financial intermediary lends or invests become the asset of the financial intermediary.
Consider two examples using financial intermediaries that we will elaborate upon further:
- A Commercial Bank: A commercial bank is a type of depository institution. Everyone knows that a bank accepts deposits from individuals, corporations, and governments. These depositors are the lenders to the commercial bank. The funds received by the commercial bank become the liability of the commercial bank. In turn, as explained later, a bank lends these funds by either making loans or buying securities. The loans and securities become the assets of the commercial bank.
- A Mutual Fund: A mutual fund is one type of regulated investment company. A mutual fund accepts funds from investors who, in exchange receive mutual fund shares. In turn, the mutual fund invests those funds in a portfolio of financial instruments. The mutual fund shares represent an equity interest in the portfolio of financial instruments and the financial instruments are the assets of the mutual fund.
Basically, this process allows a financial intermediary to transform financial assets that are less desirable for a large part of the investing public into other financial assets—their own liabilities—which are more widely preferred by the public. This asset transformation provides at least one of three economic functions:
- Maturity intermediation
- Risk reduction via diversification
- Cost reduction for contracting and information processing
There are other services that financial intermediaries can provide. They include:
- Facilitating the trading of financial assets for the financial intermediary’s customers through brokering arrangements.
- Facilitating the trading of financial assets by using its own capital to take the other position in a financial asset to accommodate a customer’s transaction.
- Assisting in the creation of financial assets for its customers and then either distributing those financial assets to other market participants.
- Providing investment advice to customers.
- Managing the financial assets of customers.
- Providing a payment mechanism.
Economic Functions of Financial Intermediaries
There are three economic functions of financial intermediaries when they transform financial assets.
- Maturity Intermediation
- Risk Reduction via Diversification
- Reducing the Costs of Contracting and Information Processing

