Table of Contents
Government Sector
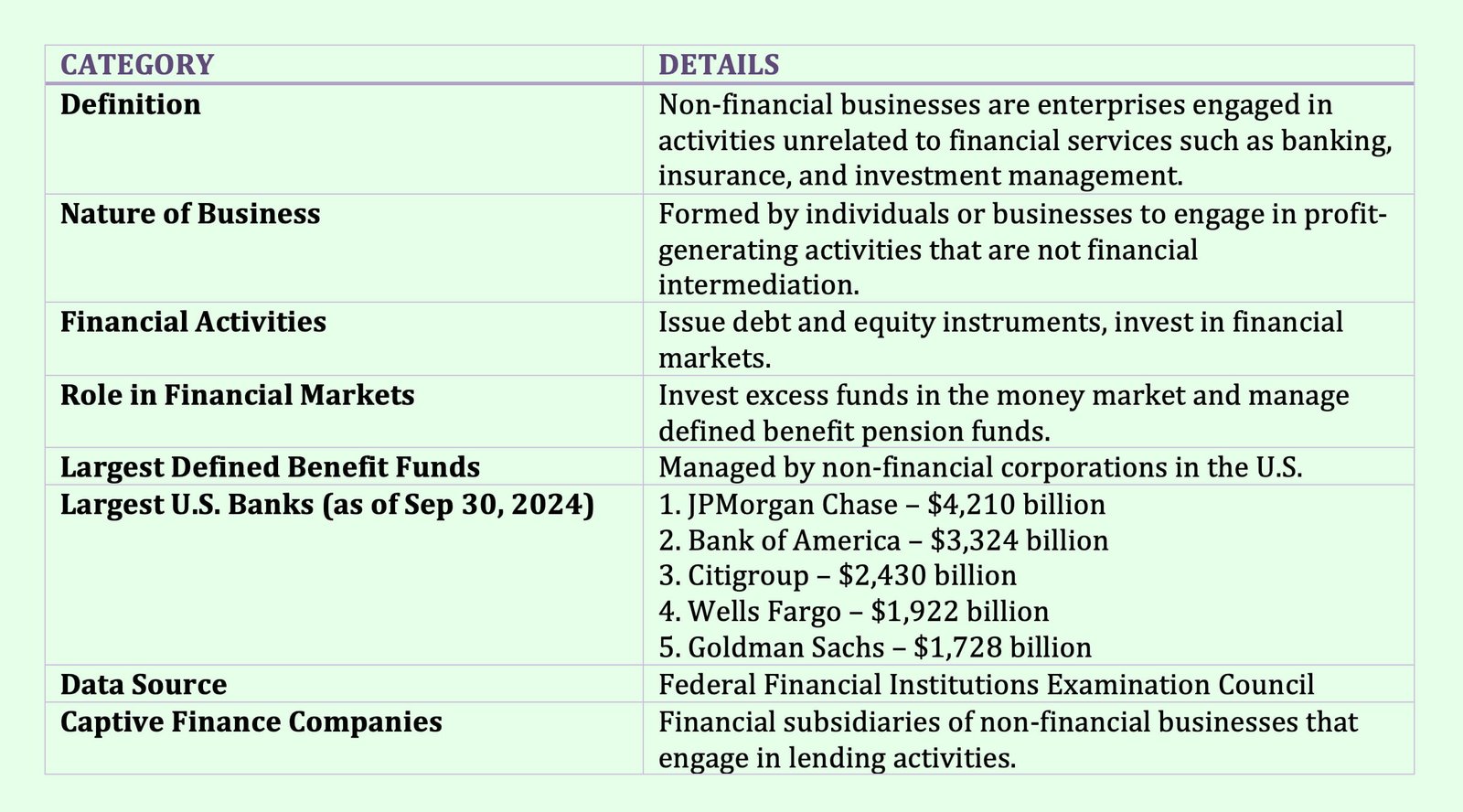
The government sector comprises organisations and institutions that operate under public administration to provide essential services, maintain law and order, and support economic stability.
The government sector includes the federal government, as well as state and local government:
- Federal Government
- Government Owned Corporations
- Government Sponsored Enterprises
- State and Local Governments
Federal Government
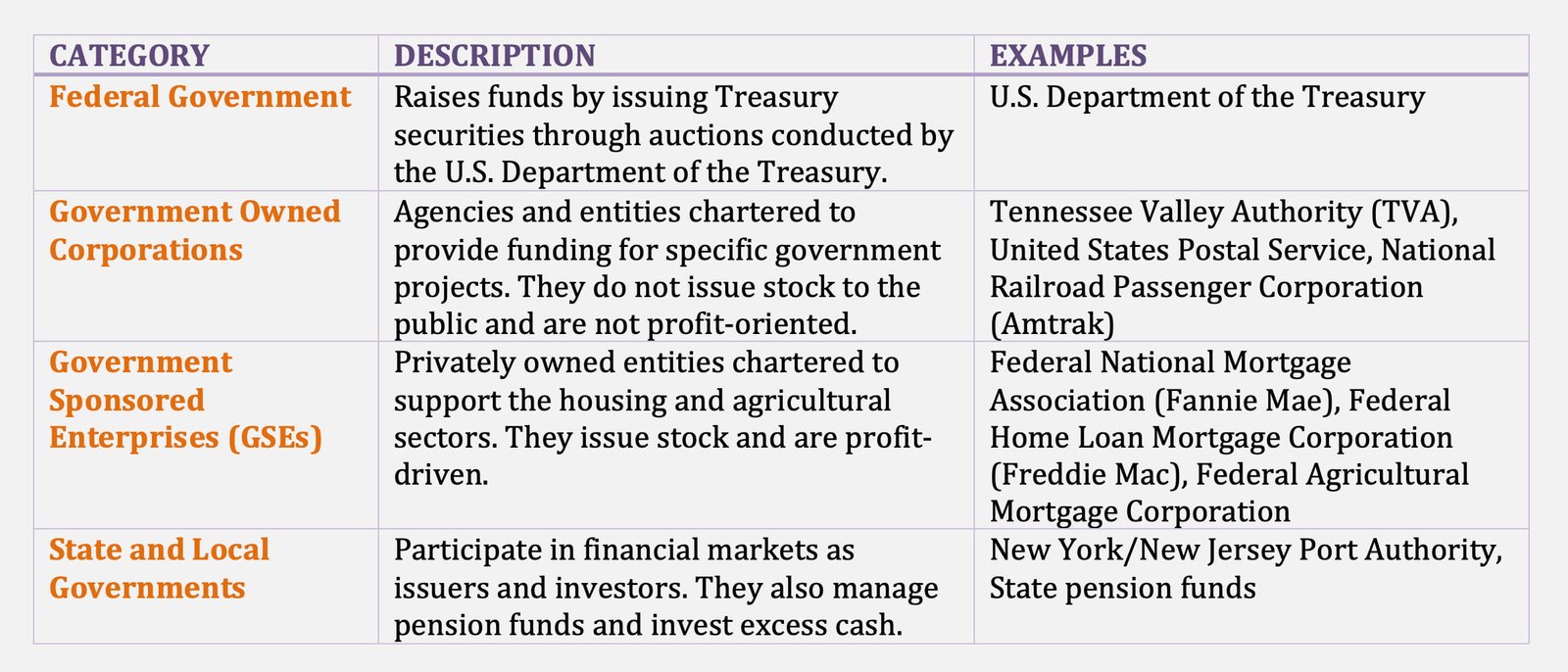
The U.S. federal government raises funds by issuing securities. The securities, referred to as Treasury securities, are issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury through an auction process.
Government Owned Corporations
The federal government has agencies that participate in the financial market by buying and selling securities. The federal government has chartered entities to provide funding for specific U.S. government projects.
These entities are called government-owned corporations. A good example is the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), which was established by Congress in 1933 primarily to provide flood control, navigation, and agricultural and industrial development, and to promote the use of electric power in the Tennessee Valley region.
Two other examples of government-owned corporations are the United States Postal Service and the National Railroad Passenger Corporation (more popularly known as Amtrak). In fact, of all the government-owned corporations, the TVA is the only one that is a frequent issuer of securities directly into the financial markets.
Other government-owned corporations raise funds through the Federal Financing Bank (FFB). The FFB is authorised to purchase or sell obligations issued, sold, or guaranteed by other federal agencies.
Government Sponsored Enterprises
Another type of government-chartered entity is one that is chartered to provide support for two sectors that are viewed as critically important to the U.S. economy: housing and agricultural sectors. These entities are government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs), and are privately owned entities.
There are two types of GSEs. The first is a publicly owned shareholder corporation whose stock is publicly traded. The publicly owned GSEs include the Federal National Mortgage Association, Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation, and Federal Agricultural Mortgage Corporation.
The first two are the most well known GSEs because of the key role that they played in the housing finance market. Both Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac have similar purposes, which are to promote home ownership through the availability of financing. They accomplish this by buying mortgages, pooling them, and selling mortgaged-backed securities to investors. Because of the financial difficulties faced by both Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, the U.S. government took control of these two GSEs by placing them into conservatorship.
The other type of GSE is a funding entity of a federally chartered bank lending system and includes the Federal Home Loan Banks and the Federal Farm Credit Banks.
Government-sponsored corporations are often confused with government-owned corporations. An important distinction is that government owned corporations do not issue stock to the public, whereas GSEs issue stock.
Another distinction is that government-owned corporations are not operated for a profit, whereas GSEs are profit-oriented. Still another distinction is that the entire board of directors of a government-owned corporation is appointed by the U.S. President, whereas only five of nine directors are appointed by the President for GSEs such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
State and Local Governments
State and local governments are both issuers and investors in the financial markets. In addition, these entities establish authorities and commissions that issue securities in the financial market. Examples include the New York/New Jersey Port Authority.
State and local governments invest when they have excess cash due to the mismatch between the timing of tax or other revenues and when those funds have to be spent. However, the major reason why they participate as investors is due to the funds available to invest from the pension funds that they sponsor for their employees.
More specifically, many state and local governments provide a defined benefit program, a form of pension where they guarantee benefits to the employees and their beneficiaries.