Table of Contents
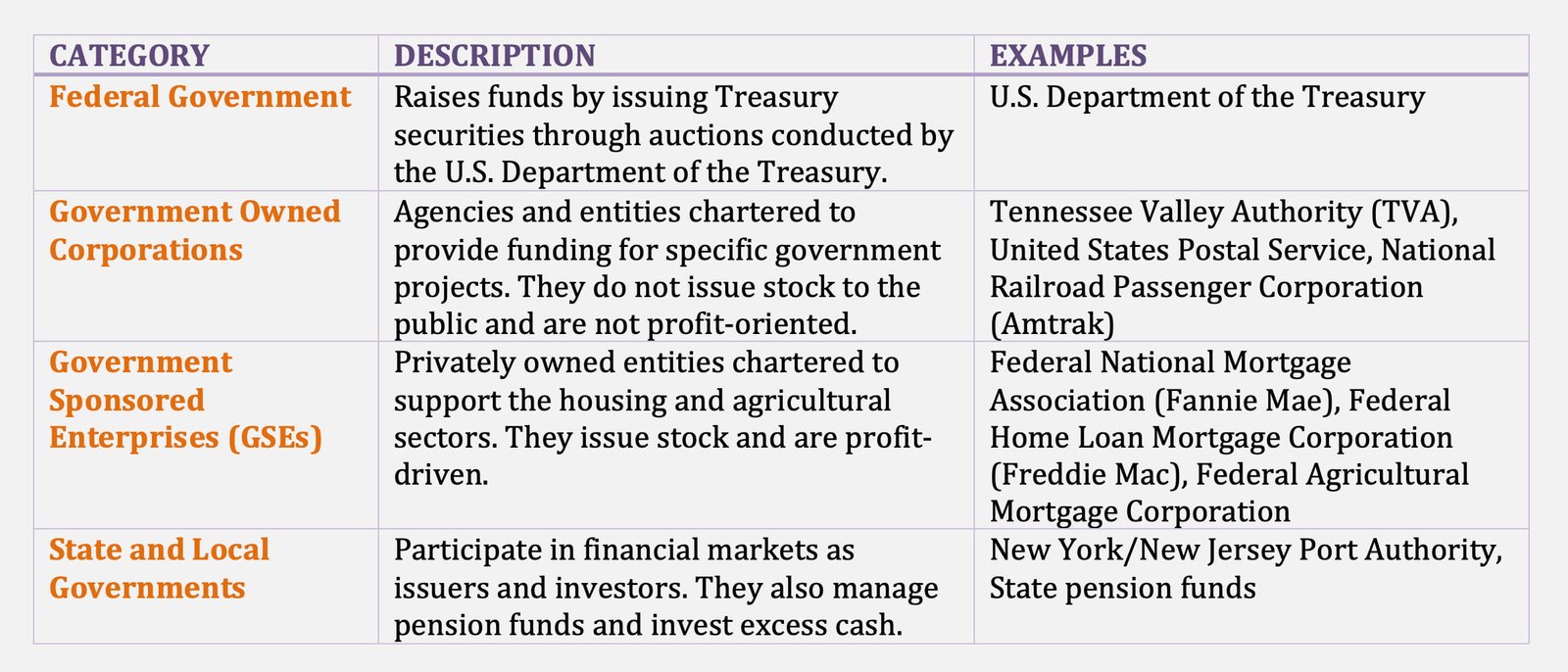
Foreign Investors
The sector referred to as foreign investors includes individuals, non-financial business, and financial entities that are not domiciled in the United States, as well as foreign central governments and supranationals.
Foreign Investors are individuals, companies, or institutions based in one country that invest capital in businesses, assets, or financial instruments in another country.
Foreign Central Bank
A foreign central bank is a monetary authority of the foreign country, such as the People’s Bank of China (PBC), the European Central Bank, and the Bank of Canada.
Foreign central banks participate in the U.S. financial market for two reasons:
- The first reason is to stabilize their currency relative to the U.S. dollar.
- The second reason is to purchase a financial instrument with excess funds because it is perceived to be an attractive investment vehicle.

Supranational Institution
A supranational institution is an international entity that is created by two or more central governments through international treaties.
We can divide supranationals into two categories: multilateral development banks and others.
The former are supranational financial institutions with the mandate to provide financial assistance with funds obtained from member countries to developing countries and to promote regional integration in specific geographical regions.
Multilateral Development Banks
The largest multilateral development banks are the European Investment Bank with more than $300 billion in total assets and the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (popularly referred to as the World Bank) with more than $250 billion in total assets
The next two largest, the Inter-American Development Bank and Asian Development Bank, have less than a third of the assets of the two largest multilateral development banks.